Plastic mulch pollution in crop soil may threaten food security
Plastic debris could harm crop health in long term Plastic mulching involves the use of thin plastic sheeting to conserve moisture and boost temperatures in soil. Commonly used in arid, cooler climates such as China, it has been shown to improve crop health and yield. With water conservation becoming an increasing global priority, plastic mulch…
Improving water storage capacity in low-quality soils in sub-Saharan Africa
A recent study published by an international team of researchers has demonstrated how the use of novel water storage technology can improve soil conditions and promote crop production in low-quality sandy soil areas.
Soil microbiome linked to disease resistance in crops
A recent study has unearthed the mystery of how plant disease resistance is linked to the soil microbiome. This new area of research will open up new possibilities for a more sustainable food production system and help combat global food security threats.
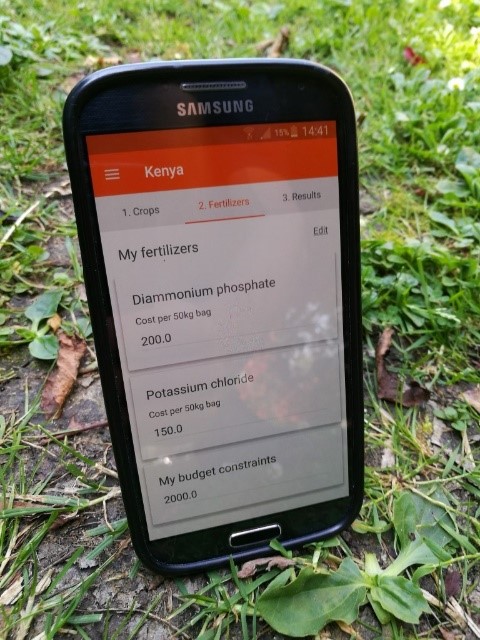
Phone app set to transform how low-income farmers in Africa invest in fertilizer
An upgrade to a mobile phone app now offers farmers across Africa even more benefits and cutting-edge fertilizer use technology. This will help farmers to grow healthier, more productive with increasingly profitable crops, as a result of more informed use of how small amounts of fertilizer impact the crops which they grow.
Amid global soil crisis, governments struggle to reach farmers
By Fatima Arkin. Reblogged from devex. To help tackle nutrient deficiency and plastic pollution in India’s soils, the country has one of the best knowledge delivery systems and trained human resource power in agriculture research. And yet, over 59 percent of the farming households receive no assistance from either their government or the private sector,…
The future for coastal farmers in Bangladesh
A recent study published in Nature Climate Change has suggested that the future global effects of climate change will impact the livelihoods of over 200,000 coastal farmers in Bangladesh as sea levels rise. Flooding of saltwater is already negatively impacting coastal residents in the country as soil conditions alter, causing farmers to either change from…